Lumbar Microdiscectomy Surgery in Allen, TX
Home > Orthopedic Spine Surgeon Allen, TX > Lumbar Microdiscectomy Surgery in Allen, TX
Specialties
Herniated discs are painful conditions that can affect the lumbar spine, leading to discomfort, numbness, and tingling. Disc herniations are fairly common in terms of spinal conditions, with about 5 to 20 per every 1,000 adults experiencing them annually. Lumbar disc herniation can severely impair one’s movement and overall quality of life. If you are suffering from a painful herniated lumbar disc, you may benefit from lumbar microdiscectomy surgery in Allen, TX.
At the Advanced Spine Center, Dr. Courtney is our skilled and highly compassionate orthopedic surgeon specializing in spinal conditions. As an orthopedic spine surgeon in Allen, he has nearly 30 years of experience treating all manner of spine ailments. To schedule an appointment with Dr. Courtney about your condition, please call our office at 972-499-5457 or submit an online intake form.
What Is a Lumbar Microdiscectomy Surgery?
A lumbar microdiscectomy is a surgical procedure performed to relieve pressure on the spinal nerves in the lumbar (lower) region of the spine. This surgery is typically used to treat a herniated disc that is causing pain, weakness, numbness, or tingling in the lower back, buttocks, or legs. It is more or less a minimally invasive lumbar discectomy that removes only a portion of a herniated disc rather than the entire affected disc.
The goal of a microdiscectomy is to alleviate pressure on the nerves and reduce pain and other symptoms associated with the herniated disc. Compared to traditional open surgery, microdiscectomy is considered less invasive because it involves smaller incisions and generally results in less damage to surrounding tissues and quicker recovery times.
Differences Between Discectomy and Microdiscectomy
Discectomy and microdiscectomy are both surgical procedures aimed at treating spinal disc problems, particularly lumbar disc herniation causing nerve compression. While they share similarities, they differ primarily in their surgical approach, invasiveness, and the equipment used during the procedure.
Lumbar Discectomy
- Procedure: In a discectomy, the surgeon removes a portion of the intervertebral disc that is causing pressure on the spinal nerves. This procedure can be performed via a traditional open surgery approach.
- Incision: Typically, a larger incision is made in the back to access the affected disc.
- Surgical Approach: Traditional discectomy often involves cutting through muscles and tissues to access the spine, leading to more disruption of surrounding structures.
- Equipment: The surgeon may or may not use a microscope or specialized instruments during the procedure.
- Invasiveness: It tends to be more invasive compared to microdiscectomy.
Lumbar Microdiscectomy
- Procedure: Microdiscectomy is a minimally invasive version of a discectomy.
- Incision: It involves making a smaller incision in the back, typically less than an inch long.
- Surgical Approach: Microdiscectomy is performed using specialized surgical instruments and often with the aid of a microscope or magnifying lenses. This allows for a more targeted approach to remove the portion of the herniated disc that’s causing nerve compression.
- Equipment: Using microscopic or magnified visualization tools allows for precision in targeting the affected area while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues.
- Invasiveness: It’s considered less invasive than traditional discectomy due to smaller incisions and less disruption of muscles and tissues.
Differences Between Spinal Fusion and Microdiscectomy
Spinal fusion and microdiscectomy are both surgical procedures performed on the spine, but they address different issues and have distinct purposes. Microdiscectomy is a minimally invasive spine surgery performed to relieve pressure on spinal nerves caused by a herniated or ruptured disc in the lumbar (lower) spinal column. It involves removing a portion of the herniated disc material that is pressing on the nerves.
Spinal fusion is a procedure aimed at stabilizing the spine by fusing two or more vertebrae together to eliminate motion between them. It’s commonly used to treat various spinal conditions, including spinal deformities, instability, fractures, degenerative disc disease, or severe disc herniation that hasn’t responded to other treatments.
Differences Between Lumbar Injections and Microdiscectomy
The main difference between injections and microdiscectomy is that the latter is a spinal surgery, while the former is not. Lumbar injections are primarily used to manage pain and inflammation, offering temporary relief, while microdiscectomy is a surgical procedure aimed at resolving the cause of spinal nerve root compression due to a herniated disc.
Why Do We Recommend Lumbar Microdiscectomy?
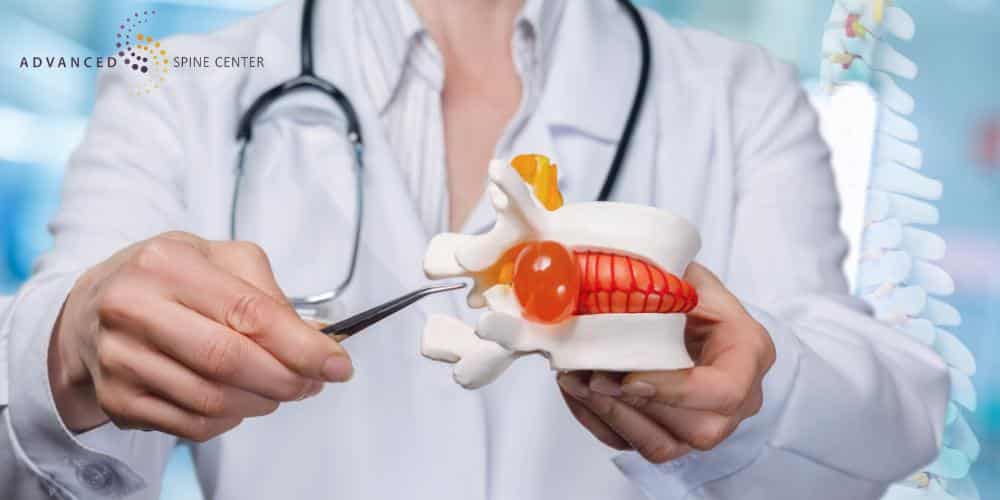
Lumbar microdiscectomy is recommended for individuals experiencing symptoms related to a herniated lumbar disc when conservative treatments have failed to alleviate their symptoms. Symptoms can include chronic low back pain, leg pain, and numbness. We also recommend microdiscectomy in the following cases.
Nerve Compression: A herniated disc can press on nearby nerves, causing significant pain and functional limitations. Microdiscectomy is recommended to directly address the source of nerve compression and alleviate symptoms by removing the portion of the disc that’s causing the pressure.
Functional Impairment: If the symptoms significantly impair a person’s ability to perform daily activities, work, or maintain their quality of life, surgery may be suggested to help restore function and reduce pain.
Diagnostic Confirmation: In cases where diagnostic tests such as MRI or CT scans confirm the presence of a herniated disc that correlates with the patient’s symptoms, surgery might be recommended to address the specific disc-related issue.
Patient Preference: In some cases, patients may prefer a more definitive solution to their persistent and debilitating symptoms rather than continuing with non-surgical treatments that have not provided significant relief.
What Conditions Does Lumbar Microdiscectomy Treat?
Lumbar microdiscectomy is primarily used to treat conditions that involve pressure on the spinal nerves due to a herniated or ruptured disc in the lumbar (lower) spine. The procedure aims to alleviate symptoms caused by this nerve compression. Conditions that may be treated with lumbar microdiscectomy include the following.
Lumbar Herniated Discs: A herniated disc occurs when the soft inner material of a spinal disc protrudes through the tough outer layer, irritating or compressing nearby nerves.
Ruptured Discs: Similar to a herniated disc, a ruptured disc involves a tear in the disc’s outer layer, allowing the inner material to leak out and potentially compress nerves.
Sciatica: Sciatica refers to pain, weakness, numbness, or tingling that radiates along the path of the sciatic nerve, typically down the buttock and leg. This condition often arises due to compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve by a herniated or ruptured lumbar disc.
Degenerative Disc Disease: In some cases of severe degenerative disc disease where conservative treatments fail to provide relief and nerve compression is a major factor, microdiscectomy may be considered to address the specific disc-related issue causing symptoms.
How Can Patients Prepare for Microdiscectomy Surgery?
Preparing for lumbar disc surgery begins with scheduling a consultation with your doctor. Patients should have a thorough discussion with their surgeon about the procedure, its benefits, potential risks, and expected outcomes. Understanding the surgery and having realistic expectations are crucial.
Complete any pre-operative tests or examinations as recommended by the surgeon. This might include blood tests, imaging scans (MRI, CT scan), and other evaluations to ensure the patient’s readiness for surgery.
Inform your surgeon about all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Some might need to be adjusted or stopped before surgery to reduce the risk of complications. If you smoke or consume alcohol, your surgeon might recommend stopping these habits before surgery to promote better healing and reduce the risk of complications.
Maintain a healthy diet and stay well-hydrated before surgery. Good nutrition and hydration can aid in the healing process. Engage in light exercises or activities as recommended by your healthcare provider to maintain strength and mobility before surgery. However, avoid strenuous activities that might exacerbate your symptoms.
Arrange your home environment to ensure a comfortable and convenient recovery after the surgery. This might involve setting up your living space to accommodate limited mobility, arranging help if needed, and preparing meals in advance.
What Should I Expect During Microdiscectomy Lumbar Surgery?
During lumbar microdiscectomy, your surgeon will use specialized tools and techniques to alleviate pressure on the spinal nerves within the spinal canal. The general steps involved in a minimally invasive lumbar discectomy are as follows.
Anesthesia: You will be given anesthesia to ensure you are comfortable and pain-free during the surgery. The type of anesthesia used will depend on your specific case and the preferences of your surgical team.
Incision: The surgeon will make a small incision in your lower back, typically less than an inch long, to access the affected area of the spine.
Muscle Separation: Muscles around the spine are gently moved aside or retracted to provide the surgeon access to the targeted area.
Visualization: The surgeon may use a surgical microscope or magnifying lenses to enhance visibility and precision during the procedure.
Disc Removal: Using specialized instruments, the surgeon will carefully remove the part of the herniated or ruptured disc that is pressing on the spinal nerves. This part of the disc is often causing the symptoms.
Nerve Decompression: Once the problematic disc material is removed, the spinal nerves are decompressed, relieving pressure and allowing them to function without obstruction.
Closing the Incision: After the necessary disc material is removed, the muscles are returned to their original position, and the incision is closed with stitches or surgical tape.
Types of Surgical Approaches for Lumbar Microdiscectomy
There are various surgical approaches used in performing lumbar microdiscectomy. Two notable methods include percutaneous endoscopic lumbar microdiscectomy (PELD) and tubular microdiscectomy. We outline the differences between each below.
Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Microdiscectomy (PELD)
Procedure: Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy involves minimally invasive techniques that use a thin tube-like instrument with a camera (endoscope) and specialized surgical tools to access and treat the affected disc through small incisions.
Endoscopic Visualization: The surgeon guides the endoscope through a small incision, allowing visualization of the surgical site on a monitor. This approach provides direct visualization of the affected disc, nerves, and surrounding structures.
Minimal Tissue Disruption: PELD involves minimal disruption to muscles and tissues as the surgeon works through the natural openings in the spine. It aims to target the herniated disc material while preserving surrounding structures.
Advantages: This approach can potentially lead to smaller incisions, less postoperative pain, quicker recovery, and reduced damage to surrounding tissues compared to traditional open surgery.
Tubular Microdiscectomy
Procedure: Tubular microdiscectomy also utilizes minimally invasive discectomy techniques, such as a tubular retractor system, to access the affected disc.
Tubular Retractor: A tubular retractor, which is a small tube-like device, is inserted through a small incision. It gradually expands, creating a pathway to the affected area while gently pushing aside muscles and tissues.
Visualization and Instrumentation: Specialized instruments are inserted through the tubular retractor to remove the herniated disc material while the surgeon views the area using a microscope or endoscope.
Reduced Tissue Trauma: Similar to PELD, tubular microdiscectomy aims to minimize disruption to muscles and tissues surrounding the spine, potentially leading to quicker recovery times and less postoperative discomfort.
What Can Patients Expect from Lumbar Microdiscectomy Recovery?
Recovery from lumbar microdiscectomy varies between patients. However, you can generally expect the following recovery timeline.
Immediate Postoperative Period
In most cases, lumbar microdiscectomy is performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing patients to return home on the same day. However, some may require an overnight stay for monitoring.
You may experience some pain or discomfort at the surgical site. Your healthcare team will provide pain medications or other treatments to manage postoperative pain.
Initial Recovery at Home
Your surgeon will likely recommend restrictions on certain activities, such as heavy lifting, bending, or twisting, for a few weeks following surgery. Gradually, you’ll be encouraged to increase your activity level.
Proper wound care instructions will be provided to ensure the surgical incision heals properly. Keeping the incision area clean and dry is essential to prevent infection.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Physical therapy or rehabilitation may be recommended to help restore strength, flexibility, and mobility. The therapist will guide you through exercises and activities tailored to your recovery needs.
Regular follow-up appointments with your surgeon will be scheduled to monitor your progress and ensure proper healing.
Return to Normal Activities
The timeline for a full return to normal activities varies, but many individuals can gradually resume light activities within a few weeks and may return to work within a few weeks to a few months, depending on the type of job and the individual’s recovery progress.
What Are the Potential Risks and Complications of Microdiscectomy Lumbar Surgery?

Like any surgical procedure, lumbar microdiscectomy carries potential risks and complications, although they are relatively uncommon. It’s important for patients to discuss these risks with their spine surgeons to have realistic expectations about the procedure.
While complications are uncommon, some potential complications include the following.
- Bleeding: Excessive bleeding during or after the surgery is possible but rare.
- Infection: Infections at the surgical site or in deeper tissues can occur. Antibiotics are often administered before and after surgery to reduce the risk. Signs of infection include increased pain, redness, swelling, or drainage from the incision site.
- Nerve damage: While the goal of microdiscectomy is to relieve nerve compression, there is a small risk of inadvertent damage to nearby nerves during the surgery, leading to new or worsened symptoms. This risk is minimized with careful surgical techniques.
- Dural tears: Accidental tearing of the covering of the spinal cord (dura) may occur, leading to a leak of cerebrospinal fluid. This might require further treatment or repair.
- Recurrent disc herniation: In some cases, the disc may herniate again after surgery, leading to recurrent symptoms. This might necessitate further treatment or lumbar revision surgery.
- Blood clots: Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or blood clots in the legs can occur postoperatively.
- Scar tissue formation: Scar tissue can develop around the surgical site and sometimes around nerves, potentially leading to pain or irritation.
Call the Advanced Spine Center for Lumbar Microdiscectomy Surgery in Allen, TX
If you have a herniated or ruptured disc that’s keeping you from living life to the fullest, the Advanced Spine Center has you covered. We offer a wide range of conservative and surgical treatments for a wide variety of spinal conditions. To speak with a qualified medical professional about your symptoms, call our office at 972-499-5457 today.


