Specialties
Table of Contents
Facet Joint Pain Treatment in Plano, TX
At the Advanced Spine Center, cutting-edge expertise meets compassionate care in the realm of orthopedic spine surgery. If you’re seeking information on facet arthropathy treatments, you’ve come to the right place. Facet arthropathy, also known as facet syndrome, is a condition characterized by the degeneration of the facet joints in the spine. It can cause debilitating pain and restrict mobility.
At the Advanced Spine Center, our dedicated team of skilled orthopedic specialists is committed to providing facet arthropathy treatment to alleviate discomfort, enhance function, and improve your overall quality of life. To schedule an appointment with us, please call our office at 972-499-5457 today.
What Is Facet Arthropathy?
Facet arthropathy, also called facet joint syndrome, is a medical condition that involves the degeneration and deterioration of the facet joints in the spine. These small, paired joints are crucial in providing stability and facilitating smooth movement between adjacent vertebrae.
Over time, factors such as aging, wear and tear, or injury can contribute to the breakdown of the cartilage within these joints, leading to facet arthropathy. This degeneration may result in inflammation, stiffness, and, most notably, persistent back pain.
Facet arthropathy commonly affects the lumbar and cervical regions of the spine, impacting an individual’s mobility and overall quality of life. Understanding the nature of facet arthropathy is crucial for seeking appropriate medical guidance and exploring effective treatment options to manage its symptoms.
Is Facet Arthropathy a Disability?
Facet arthropathy itself is not classified as a disability, but the symptoms of facet joint syndrome can significantly impact an individual’s ability to perform daily activities, work, and maintain a good quality of life. The severity of facet arthropathy varies from person to person, and while some may experience mild discomfort, others may face chronic pain and functional limitations. In cases where the symptoms are severe and persistent, individuals may find it challenging to engage in regular work duties or daily tasks, potentially leading to disability.
Types of Facet Arthropathy
Facet arthropathy can manifest in various regions of the spine, and the affected area often determines the specific type. For example, lumbar facet joint pain can arise in the lumbar region of the spine. The most common types of facet arthropathy include the following.
Facet Arthropathy Lumbar
Lumbar facet arthropathy occurs when the lumbar facet joints in the lumbar spine undergo degeneration. This can result in lower back pain, stiffness, and reduced flexibility. Lumbar facet arthropathy is often associated with activities that place stress on the lower back, such as bending and twisting.
Cervical Facet Arthropathy
Cervical facet arthropathy affects the facet joints in the neck (cervical spine). Facet joint degeneration in this region can lead to neck pain, headaches, and restricted neck movement. Poor posture, repetitive neck movements, or trauma may exacerbate cervical facet arthropathy.
Bilateral Facet Arthropathy
Bilateral facet arthropathy occurs when facet joint disorders affect both sides of the spine. This can happen in the lumbar or cervical regions. Bilateral involvement may intensify symptoms, leading to more widespread pain and reduced function on both sides of the affected area.
Multilevel Facet Arthropathy
Multilevel facet joint disease refers to the condition where degeneration occurs in multiple levels of the spine. This can involve adjacent vertebrae at different levels, contributing to a broader range of symptoms and potentially impacting various aspects of spinal function. Multilevel facet arthropathy often requires a comprehensive treatment approach to address the different affected areas.
Stages of Facet Arthropathy
This condition is a deterioration of the facet joints, which help stabilize the spine and limit excessive motion. The facet joints are lined with cartilage and are surrounded by a lubricating capsule that enables the vertebrae to bend and twist.
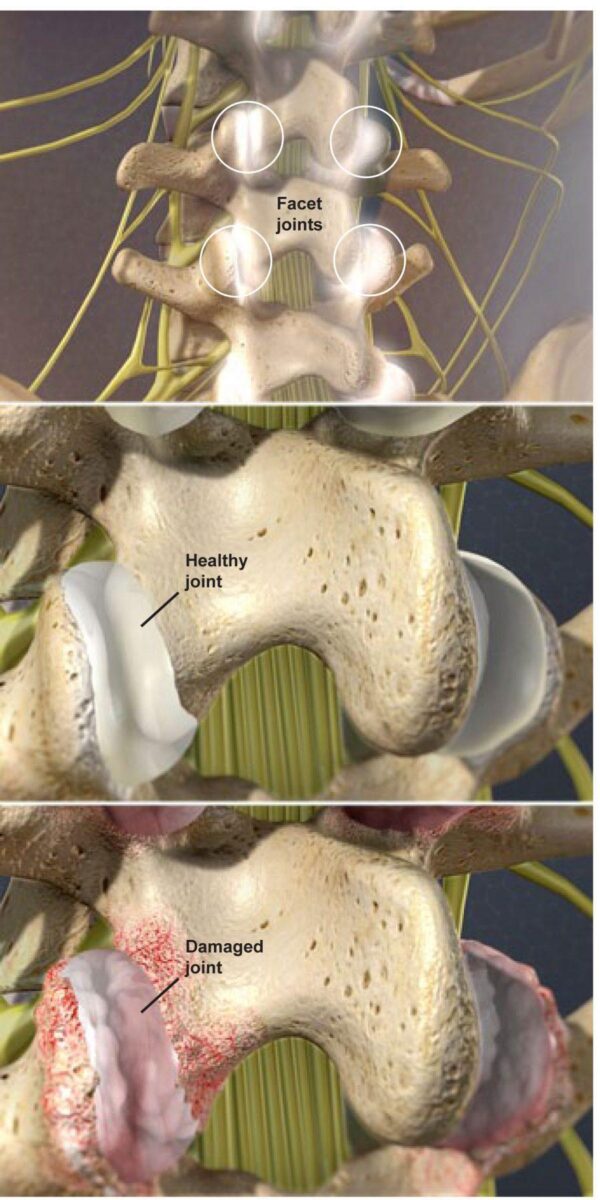
Joint Damage
Facet joint syndrome occurs when the facet joints become stressed and damaged. This damage can occur from everyday wear and tear, injury to the back or neck or because of degeneration of an intervertebral disc.
Cartilage Loss
The cartilage that covers the stressed facet joints gradually wears away. The joints become swollen and stiff. The vertebral bones rub directly against each other, which can lead to the growth of bone spurs along the edges of the facet joints.
Symptoms of Facet Arthropathy
Facet arthropathy can manifest with a range of symptoms, and the severity and specific nature of these symptoms can vary among individuals. Common symptoms of facet arthropathy may include the following.
- Localized pain, such as neck pain or lower back pain
- Pain with movement
- Stiffness
- Reduced range of motion
- Radiating pain
- Headaches
- Muscle spasms
- Tenderness
Cervical Facet Arthropathy Symptoms
Pain from facet joint syndrome differs depending on which region of the spine is damaged. If the cervical, or upper spine is affected, pain may be felt in the neck, shoulders, and upper or middle back. The person may also experience headaches.
Lumbar Facet Arthropathy Symptoms
Lumbar facet joint pain is characterized by symptoms primarily affecting the lower back and lumbar spine. Individuals with lumbar facet arthropathy commonly experience localized pain in the lower back, often exacerbated by movements such as bending, twisting, or prolonged periods of sitting or standing.
Stiffness and reduced flexibility in the lumbar region are also prevalent, with symptoms typically worsening after periods of inactivity. In some cases, lumbar facet arthropathy may lead to radiating pain down the legs if nearby spinal nerves are affected. Muscle spasms and tenderness in the lumbar area are additional indicators.
Does Facet Joint Pain Go Away?

Facet joint pain can vary in duration and may be influenced by factors such as the underlying cause, the severity of joint degeneration, and the effectiveness of treatment. In some cases, facet joint pain may resolve on its own or with conservative treatments, while in other instances, it may persist or require more extensive interventions.
Conservative treatments are often employed to manage and alleviate pain. These measures can help reduce inflammation, improve mobility, provide pain relief, and address associated symptoms. Additionally, adopting a regular exercise routine and maintaining a healthy lifestyle may contribute to long-term pain management.
However, if facet joint pain is caused by advanced joint degeneration or other underlying spinal conditions, and conservative measures are not sufficient, more invasive treatments or surgical interventions may be considered.
What Is the Treatment for Facet Arthropathy?
Facet joint syndrome is first treated conservatively with rest, ice, heat, anti-inflammatory medications, and physical therapy. In addition, facet joint blocks may be administered not only to diagnose facet joint pain but also to provide facet joint pain relief. If non-surgical methods fail to relieve pain, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Conservative Treatment Options
- Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises and stretches can improve flexibility, strengthen supportive muscles, and promote proper spinal alignment.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or analgesics may be prescribed to manage pain and reduce inflammation.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adjustments to activities, posture, and ergonomics can minimize stress on the facet joints.
- Facet Joint Injections: Steroid injections into the facet joints can provide temporary relief by reducing inflammation and alleviating pain.
- Medial Branch Blocks: These injections target the nerves that transmit pain signals from the facet joints, helping to diagnose and manage pain in the affected joint.
Surgery for Facet Joint Pain
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): RFA is a nerve ablation procedure. It uses heat generated by radiofrequency waves to disrupt the nerves transmitting pain signals from the facet joints, providing longer-lasting pain relief.
- Facet Joint Denervation: In this procedure, nerves transmitting pain signals from the facet joints are selectively targeted and disrupted, providing long-term pain relief.
- Spinal Fusion: For severe cases or when instability is present, spinal fusion may be recommended to stabilize the affected vertebral segments.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is a key component in the comprehensive management of facet joint arthritis. Through targeted exercises and stretches, physical therapy aims to strengthen the muscles supporting the spine, improve flexibility, and correct postural issues that may contribute to facet joint stress.
A physical therapist works with individuals to design personalized exercise regimens that address specific symptoms and limitations. These exercises not only help alleviate pain and inflammation but also enhance overall spine function.
Additionally, physical therapists educate patients on proper body mechanics and ergonomics, empowering them to make lifestyle adjustments that reduce strain on the facet joints. By promoting core stability and improving biomechanics, physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing facet joint pain and fostering long-term spinal health.
Facet Joint Pain Exercises to Avoid

While exercise is generally beneficial for managing facet joint pain, certain activities may exacerbate symptoms and should be approached with caution or avoided altogether. Individuals with facet joint pain should consider avoiding or modifying exercises that place excessive strain on the spine or cause excessive twisting and compression of the facet joints. Some exercises to avoid include the following.
- Heavy weight lifting
- High-impact activities
- Excessive forward bending
- Twisting movements
- Unsupported spinal extension
- Deep backbends
How to Sit with Facet Joint Pain
Sitting with facet joint pain requires adopting a posture that minimizes stress on the spine. Begin by choosing a chair with proper lumbar support to maintain the natural curve of the lower back. Sit back in the chair, ensuring your back is well-supported, and consider using a small cushion or rolled-up towel at the lower back for additional support. Keep both feet flat on the floor, knees bent at a 90-degree angle, and avoid crossing your legs.
Distribute your body weight evenly on both hips and sit back in the chair, rather than slouching or leaning forward. Take breaks to stand and stretch periodically, incorporating gentle movements to prevent stiffness. Utilizing ergonomic furniture and maintaining good sitting habits can provide pain relief and promote a more comfortable seated experience.
What Aggravates Facet Joint Pain?
Facet joint pain can be aggravated by various factors and activities that place stress on the facet joints or contribute to their degeneration. Some common aggravating factors include the following.
- Poor posture: Maintaining improper posture, such as slouching or sitting in a hunched position, can increase stress on the facet joints and worsen pain.
- Prolonged sitting: Extended periods of sitting, especially without breaks or proper lumbar support, can contribute to stiffness and aggravate facet joint pain.
- Repetitive movements: Repeated bending, twisting, or lifting without proper body mechanics can strain the facet joints and lead to increased pain.
- Inactivity: Lack of regular physical activity and sedentary behavior can lead to stiffness and reduced joint mobility, worsening facet joint pain.
- Obesity: Excess body weight places additional strain on the facet joints, contributing to their degeneration and increasing the likelihood of pain.
- Trauma or spine injury: Previous injuries or trauma to the spine can accelerate facet joint degeneration and make the joints more susceptible to pain.
- Arthritis: Conditions like osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis that affect the facet joints can exacerbate pain and inflammation.
- Dehydration: Inadequate hydration can affect the lubrication of joints, including the facet joints, potentially worsening pain and stiffness.
Facet Joint Syndrome Treatment in Plano, TX
At the Advanced Spine Center, we understand the significant impact facet arthropathy can have on your daily life. Our commitment to providing unparalleled care and cutting-edge treatments sets us apart in the realm of orthopedic spine surgery. From conservative measures, such as physical therapy and minimally invasive procedures, to advanced surgical interventions when needed, our expert team is dedicated to tailoring a comprehensive treatment plan to address your unique needs.
We strive not only to provide long-term pain relief, but to enhance your overall spinal health and improve functionality. Trust in our expertise and compassionate care as we guide you through the journey to a pain-free and vibrant life. Schedule an appointment with us today by calling 972-499-5457.

Request an Appointment
Common Patient Questions
ExcellentBased on 147 reviews
 Robert AliceaThe doctor and his staff were very welcoming and kind ..explained my issues in detail . Will highly recommend
Robert AliceaThe doctor and his staff were very welcoming and kind ..explained my issues in detail . Will highly recommend German CisnerosEvery visit to Dr. Courtney's office is educational and most beneficial. Dr. Courtney and ALL of his staff are the best!
German CisnerosEvery visit to Dr. Courtney's office is educational and most beneficial. Dr. Courtney and ALL of his staff are the best! Jamey DerryberryMy wife and I both go to Dr Courtney for back issues. Great care. Great staff. Great surgical facility and smooth process. LOVE THEM!!!
Jamey DerryberryMy wife and I both go to Dr Courtney for back issues. Great care. Great staff. Great surgical facility and smooth process. LOVE THEM!!! Mark CotterDr Courtney and his staff truly care about my well being. They are the only ones I have found that have been able to help me with my workman's comp claim
Mark CotterDr Courtney and his staff truly care about my well being. They are the only ones I have found that have been able to help me with my workman's comp claim J “JAFO”Does your back hurt? Has your back been hurting, yet no other surgeon can or won't help you; or worse tells you nothing is wrong? You're in the wrong place! I had 4 back operations with no improvement. I had an additional 6 other consultations with "there's nothing wrong with you". The truth was I was probably 2-3 months away from permanent leg and lower back paralysis. He fixed me. I can stand, I can walk. I threw away my crutches of 13 years. If you need back correction - GO SEE THIS DOCTOR! He will fix you, and fix you correctly, if it is humanly possible. Enough said! Go see him. He tells the truth and tells it like it is. 🙂
J “JAFO”Does your back hurt? Has your back been hurting, yet no other surgeon can or won't help you; or worse tells you nothing is wrong? You're in the wrong place! I had 4 back operations with no improvement. I had an additional 6 other consultations with "there's nothing wrong with you". The truth was I was probably 2-3 months away from permanent leg and lower back paralysis. He fixed me. I can stand, I can walk. I threw away my crutches of 13 years. If you need back correction - GO SEE THIS DOCTOR! He will fix you, and fix you correctly, if it is humanly possible. Enough said! Go see him. He tells the truth and tells it like it is. 🙂 Terri StewmanDr courtney and his staff are great! Dr courtney always takes his time with you and I feel he truly cares about his patients.
Terri StewmanDr courtney and his staff are great! Dr courtney always takes his time with you and I feel he truly cares about his patients. Ross WigingtonGreat Dr and helped me multiple times over the years Would recommend to anyone that needs help
Ross WigingtonGreat Dr and helped me multiple times over the years Would recommend to anyone that needs help Bridgette e MentesanaDr. Courtney is knowledgeable and takes the time to really explain what’s going on and explain why you’re in pain and the several options to correct the issue. I never felt rushed and he was on time to our appointment which is such a rare thing. The rest of the office staff was absolutely top notch. They were really down to earth and so nice, you could tell they liked their jobs and were treated well. It was a very welcoming atmosphere. I felt very comfortable and I knew I was in capable hands just by the way he treated his staff and listened to his patients. Highly recommend.
Bridgette e MentesanaDr. Courtney is knowledgeable and takes the time to really explain what’s going on and explain why you’re in pain and the several options to correct the issue. I never felt rushed and he was on time to our appointment which is such a rare thing. The rest of the office staff was absolutely top notch. They were really down to earth and so nice, you could tell they liked their jobs and were treated well. It was a very welcoming atmosphere. I felt very comfortable and I knew I was in capable hands just by the way he treated his staff and listened to his patients. Highly recommend. Marie BentonDr Courtney did my neck surgery and my 360 back surgery. I would not go to another surgeon, he cares about his patients and it shows! His staff is great as well! I trust his opinion and skills 100%
Marie BentonDr Courtney did my neck surgery and my 360 back surgery. I would not go to another surgeon, he cares about his patients and it shows! His staff is great as well! I trust his opinion and skills 100%

